[2] Sources of office blood pressure measurement error: A systematic review
Published in Physiological Measurement, 2022
Abstract
Background Accurate and reliable blood pressure (BP) measurement is important for the prevention and treatment of hypertension. The oscillometric-based office blood pressure measurement (OBPM) is widely used in hospitals and clinics, but measurement errors are common in BP measurements. There is a lack of systematic review of the sources of measurement errors.
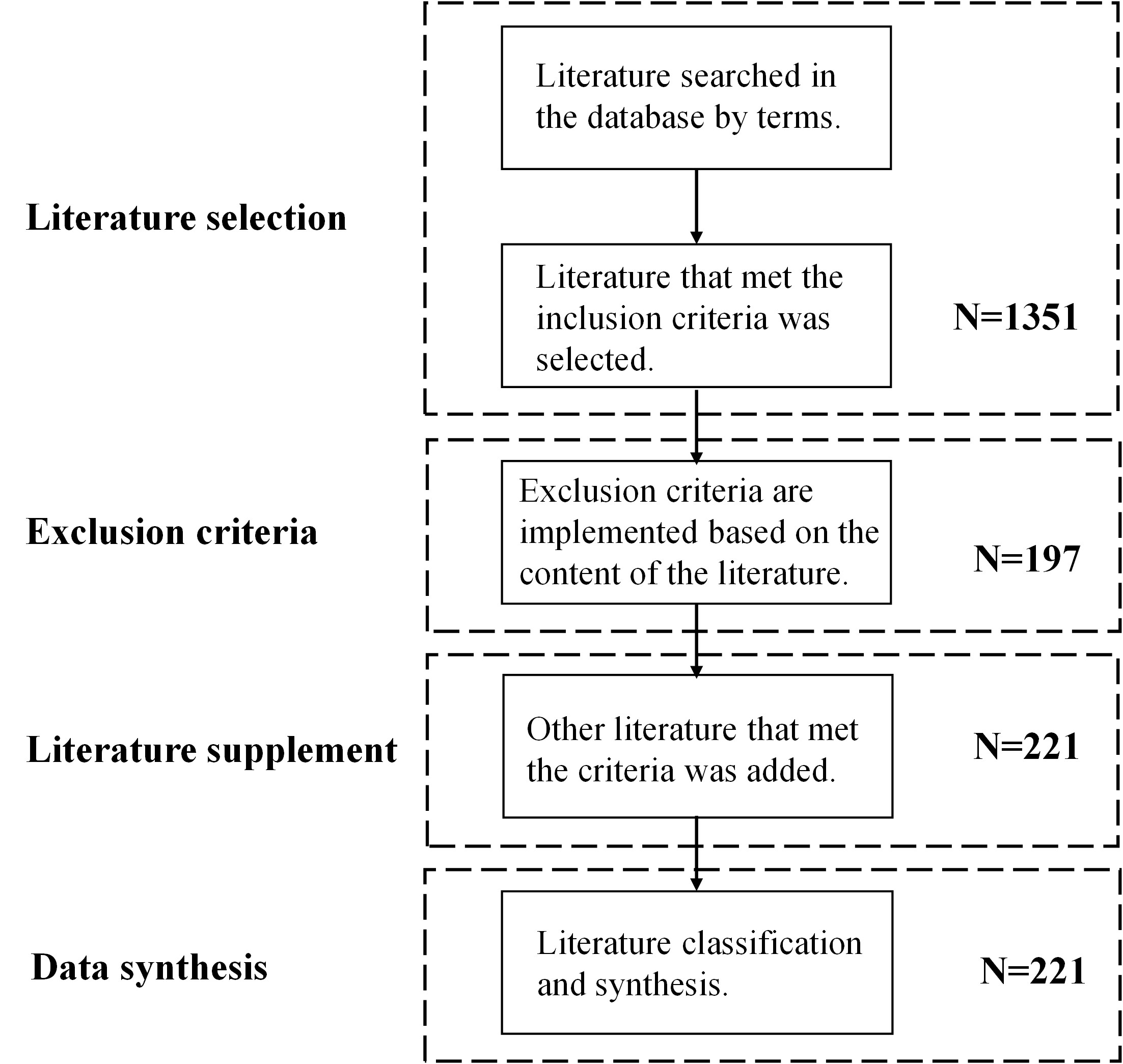
Methods A systematic review of all existing research on sources of OBPM errors. A search strategy was designed in six online databases, and all the literature published before October 2021 was selected. Those studies that used the OBPM device to measure BP from the upper arm of subjects were included.
Results A total of 1351 studies were screened, and 221 studies were included in this final review. They investigated 22 common error sources with clinical OBPM. Regarding the causes of BP errors, this review divided them into the following categories: the activities before measurement, patient’s factors, measurement environment, measurement procedure, device settings. 13 sources caused increased systolic and diastolic BP (SBP and DBP), 2 sources caused the decrease in SBP and DBP, only 1 source had no significant effect on BPs, and the other errors had a non-uniform effect (either increase or decrease in BPs). The error ranges for SBP and DBP were -14 to 33 mmHg and -6 to 19 mmHg, respectively.
Conclusions The measurement accuracy of OBPM is susceptible to the influence of measurement factors. Interpreting BP readings need to be treated with caution in clinical measurements. This review made comprehensive evidence for the need for standardized BP measurements and provided guidance for clinical practitioners when measuring BP with OBPM devices.
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, Yumin Li, Jianqing Li, Dingchang Zheng, and Chengyu Liu. "Sources of automatic office blood pressure measurement error: a systematic review." Physiological Measurement 43, no. 9 (2022): 09TR02.
Download Paper
