[3] A novel interpretable feature set optimization method in blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmography signals
Published in Biomedical Signal Processing and Controlg, 2023
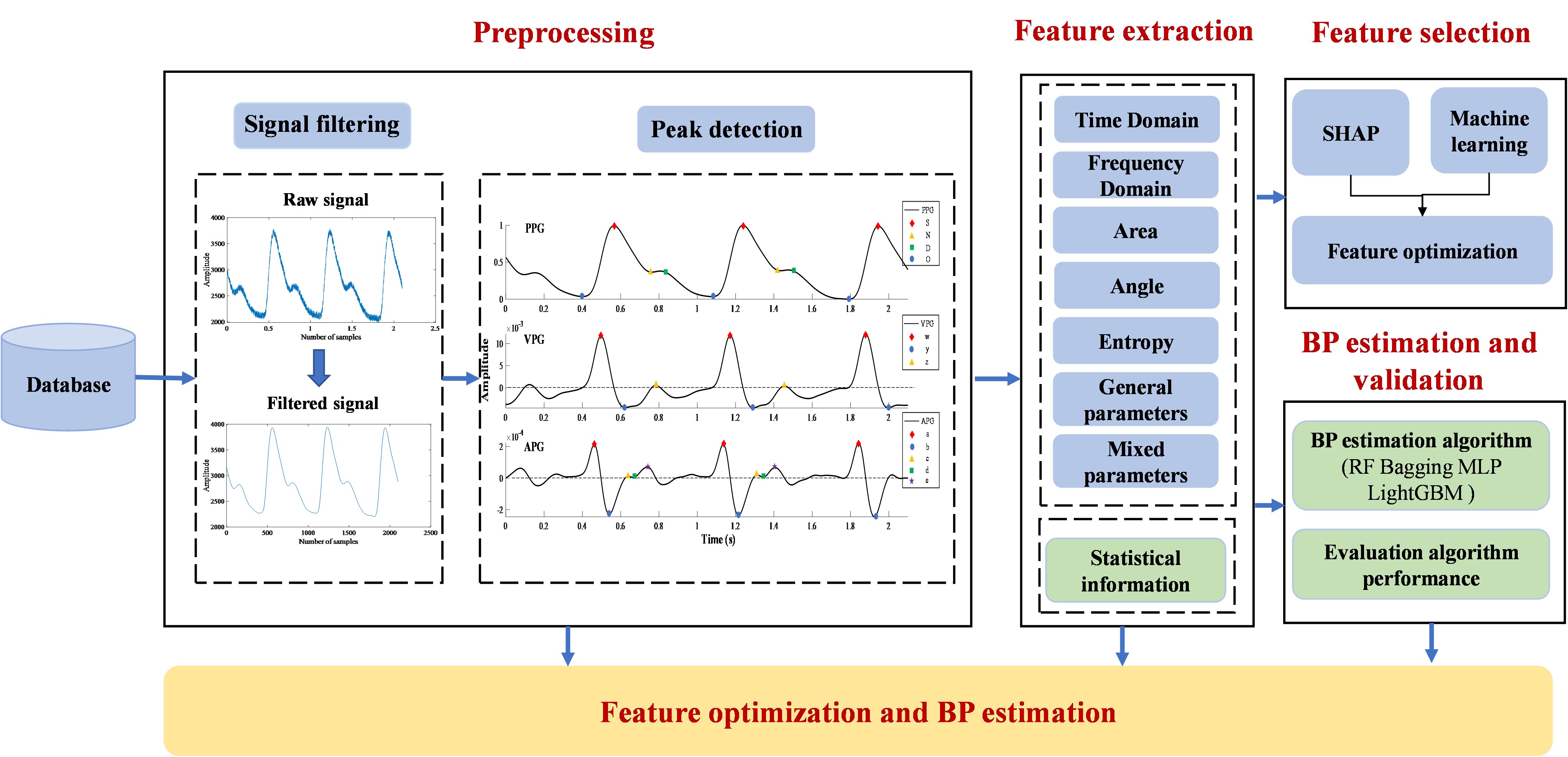
Abstract
Background Continuous blood pressure (BP) monitoring is crucial for individual health management, yet the significant inter-individual variations among patients pose challenges to achieving precision medicine.
Methods In response to this issue, we propose a parallel cross-hybrid architecture that integrates a convolutional neural network backbone and a Mix-Transformer backbone. This model, grounded in multi-view physiological signals and personalized fine-tuning strategies, aims to estimate BP, facilitating the capture of physiological information across diverse receptive fields and enhancing network expressive capabilities.
Results Our proposed architecture exhibits superior performance in estimating systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, with average absolute errors of 3.94 mmHg and 2.24 mmHg, respectively. These results surpass existing baseline models and align with the standards set by the British Hypertension Society, the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers for BP measurement. Additionally, this study explores a personalized model fine-tuning strategy by adjusting specific layers and incorporating individual information, presenting an optimal solution. The model’s generalization ability is validated through transfer learning across databases (public and self-made). To enhance the proposed architecture’s usability in wearable devices, this study employs a knowledge distillation strategy for model lightweighting, with preliminary application in our designed real-time BP estimation system.
Conclusions This study provides an efficient and accurate solution for personalized BP estimation, exhibiting broad potential applications.
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, ShuaiCong Hu, Zhijun Xiao, Qihan Hu, Daomiao Wang, and CuiWei Yang. "A novel interpretable feature set optimization method in blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmography signals." Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 86 (2023): 105184.
Download Paper
