Sitemap
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Pages
About Me
Hello, I’m Jian, a PhD student at Fudan University. Welcome to my research space!
Posts
Future Blog Post
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
publications
[1] Influence of Finger Movement on the Stability of the Oscillometric Pulse Waveform for Blood Pressure Measurement
Published in 2021 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), 2021
In medical clinics the oscillometric automated sphygmomanometer is widely used. However, there are few studies to quantify the influence of the oscillometric pulse waveform stability on the accuracy of BP values. This study addresses this issue.
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, Alan Murray, Jianqing Li, and Chengyu Liu. "Influence of finger movement on the stability of the oscillometric pulse waveform for blood pressure measurement." In 2021 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), vol. 48, pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2021.
Download Paper
[2] Sources of office blood pressure measurement error: A systematic review
Published in Physiological Measurement, 2022
A systematic review of all existing research on sources of OBPM errors. A search strategy was designed in six online databases, and all the literature published before October 2021 was selected. Those studies that used the OBPM device to measure BP from the upper arm of subjects were included.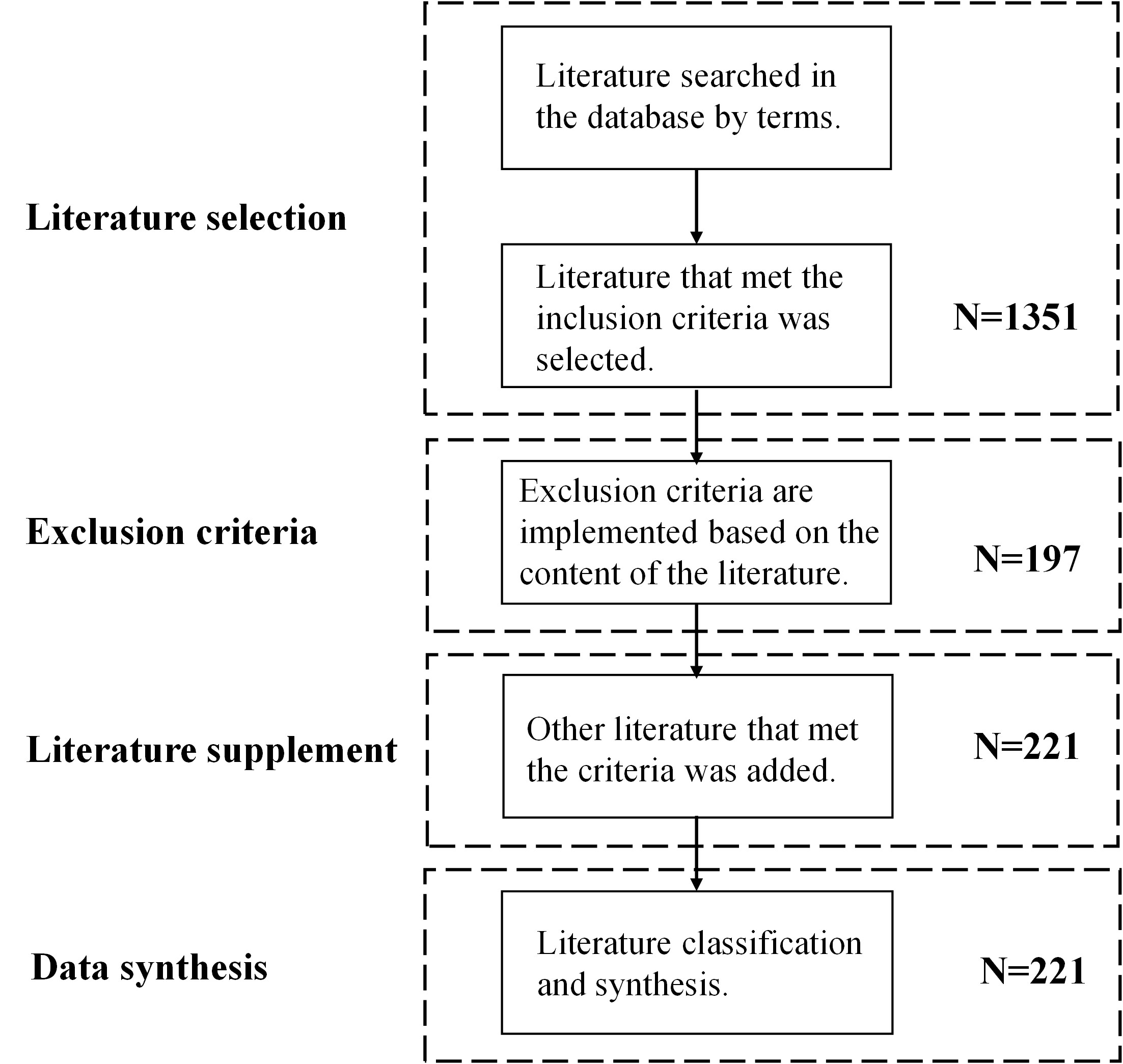
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, Yumin Li, Jianqing Li, Dingchang Zheng, and Chengyu Liu. "Sources of automatic office blood pressure measurement error: a systematic review." Physiological Measurement 43, no. 9 (2022): 09TR02.
Download Paper
[3] A novel interpretable feature set optimization method in blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmography signals
Published in Biomedical Signal Processing and Controlg, 2023
In this paper we propose a parallel cross-hybrid architecture that integrates a convolutional neural network backbone and a Mix-Transformer backbone. This model, grounded in multi-view physiological signals and personalized fine-tuning strategies, aims to estimate BP, facilitating the capture of physiological information across diverse receptive fields and enhancing network expressive capabilitie.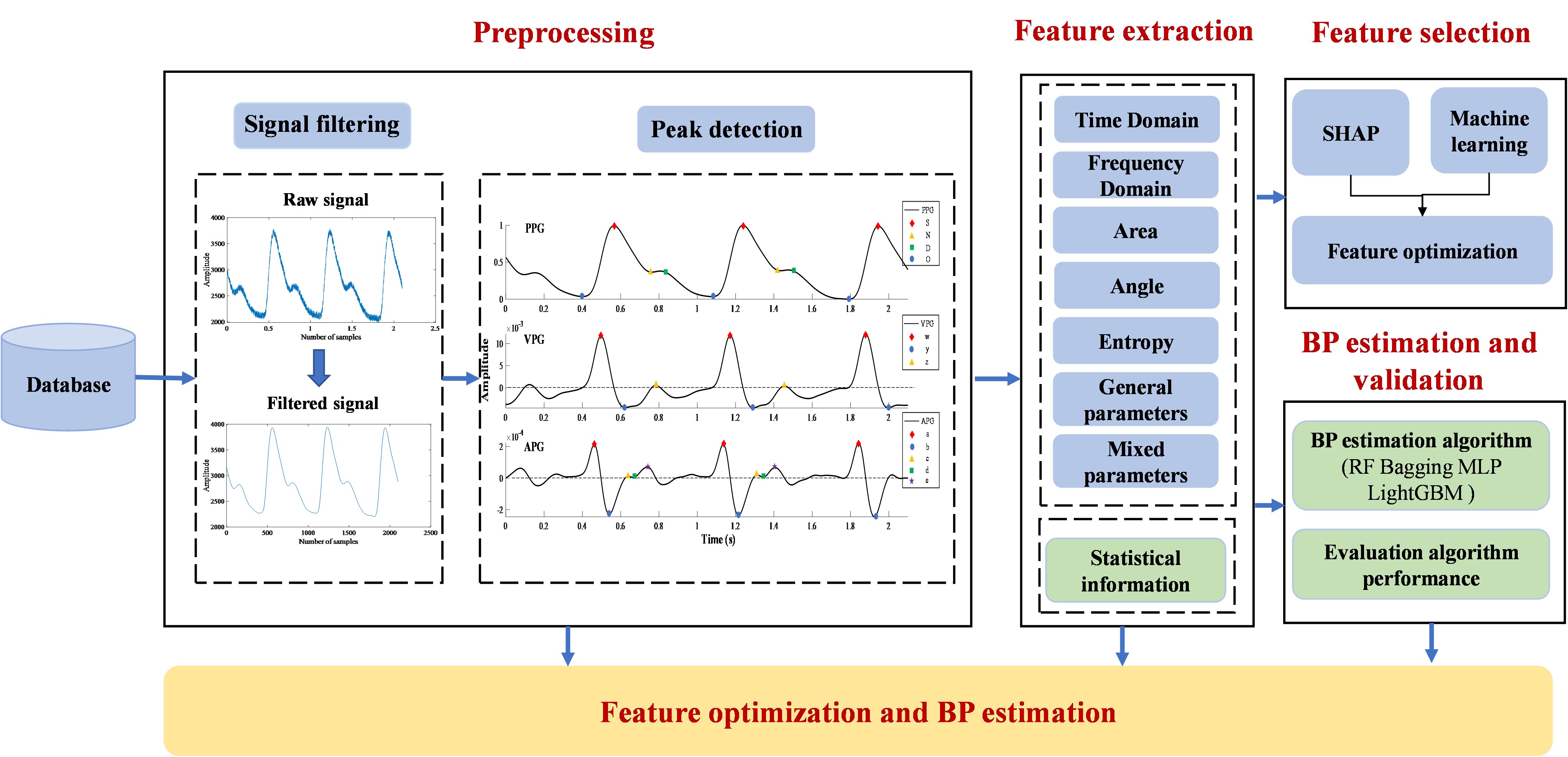
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, ShuaiCong Hu, Zhijun Xiao, Qihan Hu, Daomiao Wang, and CuiWei Yang. "A novel interpretable feature set optimization method in blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmography signals." Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 86 (2023): 105184.
Download Paper
[4] A Lightweight Hybrid Model Using Multiscale Markov Transition Field for Real-Time Quality Assessment of Photoplethysmography Signals
Published in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2023
This study introduces a lightweight model to address the imperative need for precise, real-time evaluation of PPG signal quality, followed by its deployment and validation utilizing our integrated upper computer and hardware system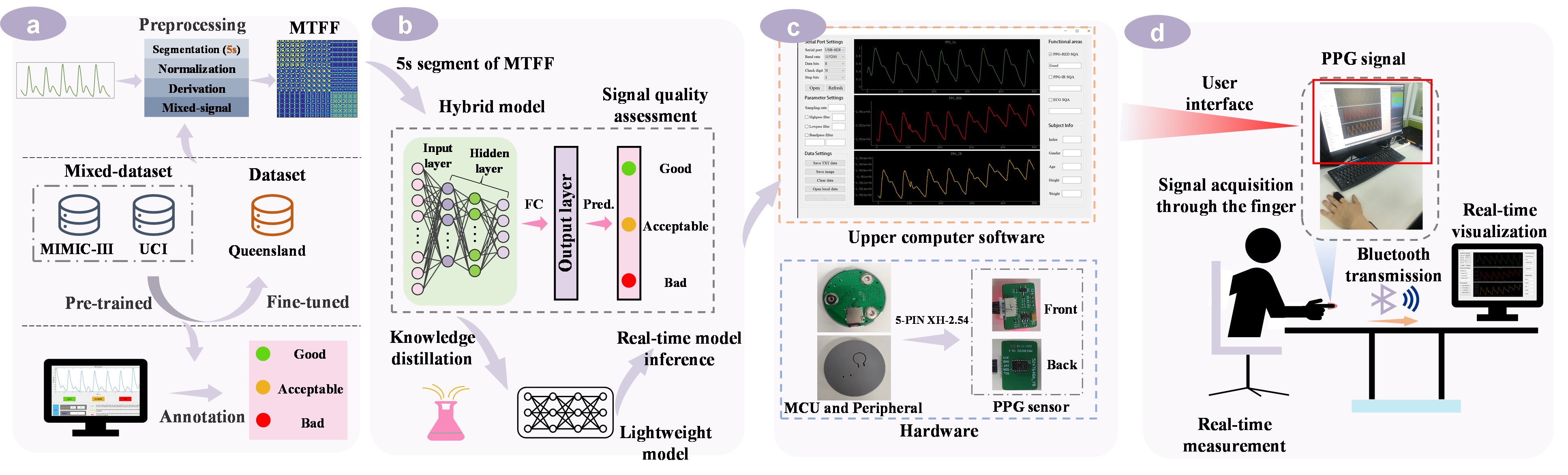
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, Shuaicong Hu, Qihan Hu, Daomiao Wang, and Cuiwei Yang. "A Lightweight Hybrid Model Using Multiscale Markov Transition Field for Real-Time Quality Assessment of Photoplethysmography Signals." IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics (2023).
Download Paper
[5] Personalized Transfer Learning for Single-Lead ECG-Based Sleep Apnea Detection: Exploring the Label Mapping Length and Transfer Strategy Using Hybrid Transformer Model
Published in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024
Two DL models, a pure convolutional neural network (CNN)-based model (PCM) and a proposed HTM, are included in the study. Eight different LMLs are considered. Furthermore, various personalized TL strategies are introduced to thoroughly explore the impact. Finally, two-sided t-tests are utilized to evaluate the significance.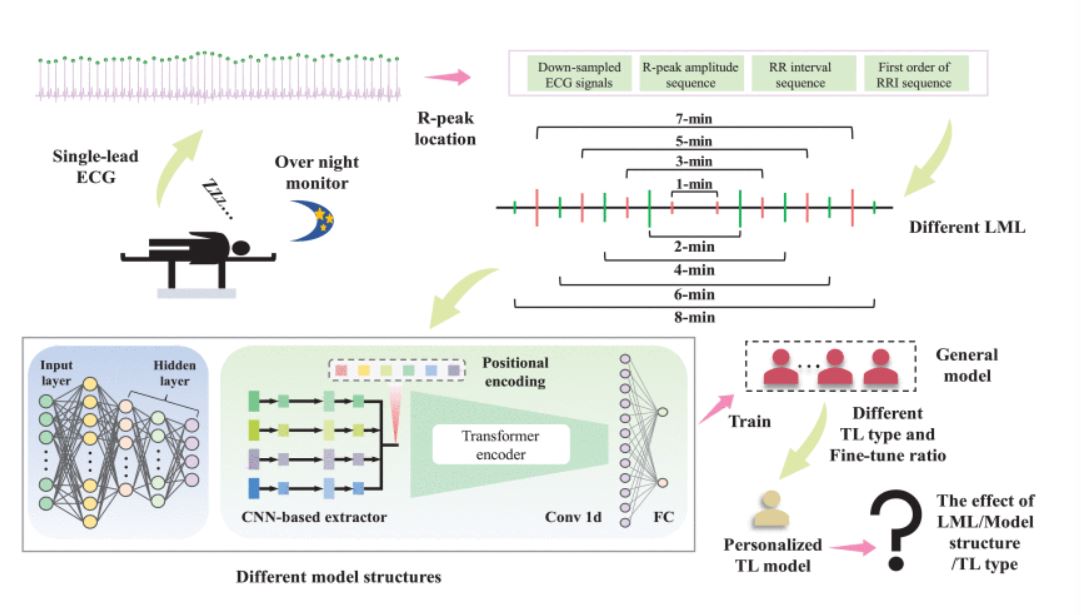
Recommended citation: Hu Shuaicong, Yanan Wang, Liu Jian, and Cuiwei Yang. "Personalized transfer learning for single-lead ecg-based sleep apnea detection: exploring the label mapping length and transfer strategy using hybrid transformer model." IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement (2023).
Download Paper
[6] Exploring the Applicability of Transfer Learning and Feature Engineering in Epilepsy Prediction Using Hybrid Transformer Model
Published in IEEE transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering, 2024
Two classical feature engineering methods and the proposed method which consists of various EEG rhythms are explored, then a hybrid Transformer model is designed to evaluate the advantages over pure convolutional neural networks (CNN)-based models. Finally, the performances of two model structures are analyzed utilizing patient-independent approach and two TL strategies.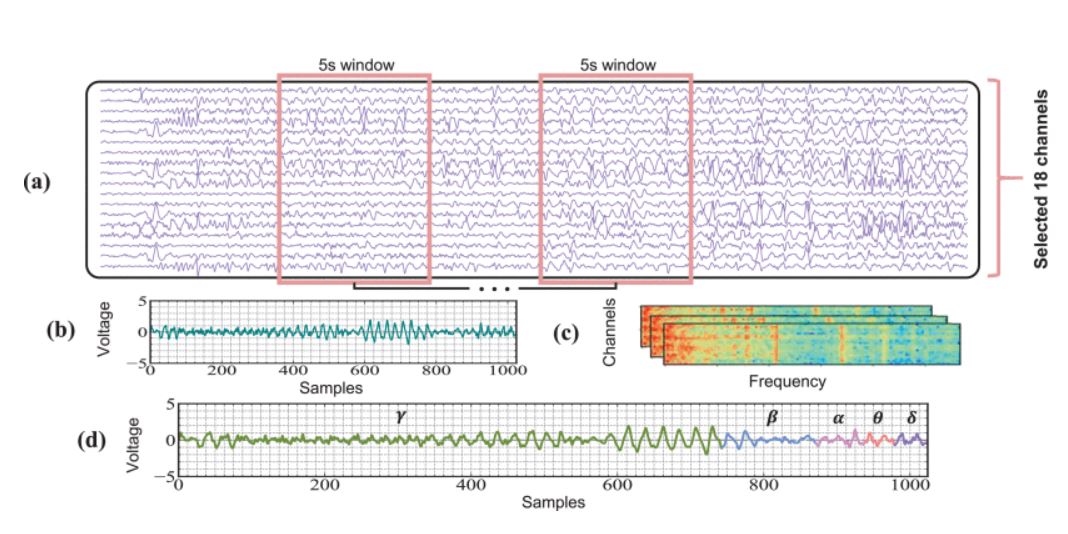
Recommended citation: Hu Shuaicong, Liu Jian, Rui Yang, Ya’Nan Wang, Aiguo Wang, Kuanzheng Li, Wenxin Liu, and Cuiwei Yang. "Exploring the applicability of transfer learning and feature engineering in epilepsy prediction using hybrid transformer model." IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 31 (2023): 1321-1332.
Download Paper
[7] Semi-Supervised Learning for Low-Cost Personalized Obstructive Sleep Apnea Detection Using Unsupervised Deep Learning and Single-Lead Electrocardiogram
Published in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2024
We utilize a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based auto-encoder (AE) with a modified training objective to detect anomalous region of OSA. An indicator based on model outputs is utilized as a benchmark measure to assign pseudo-labels with confidence to each sample. Finally, we perform validation of the semi-supervised algorithm on the same database and cross-database scenarios.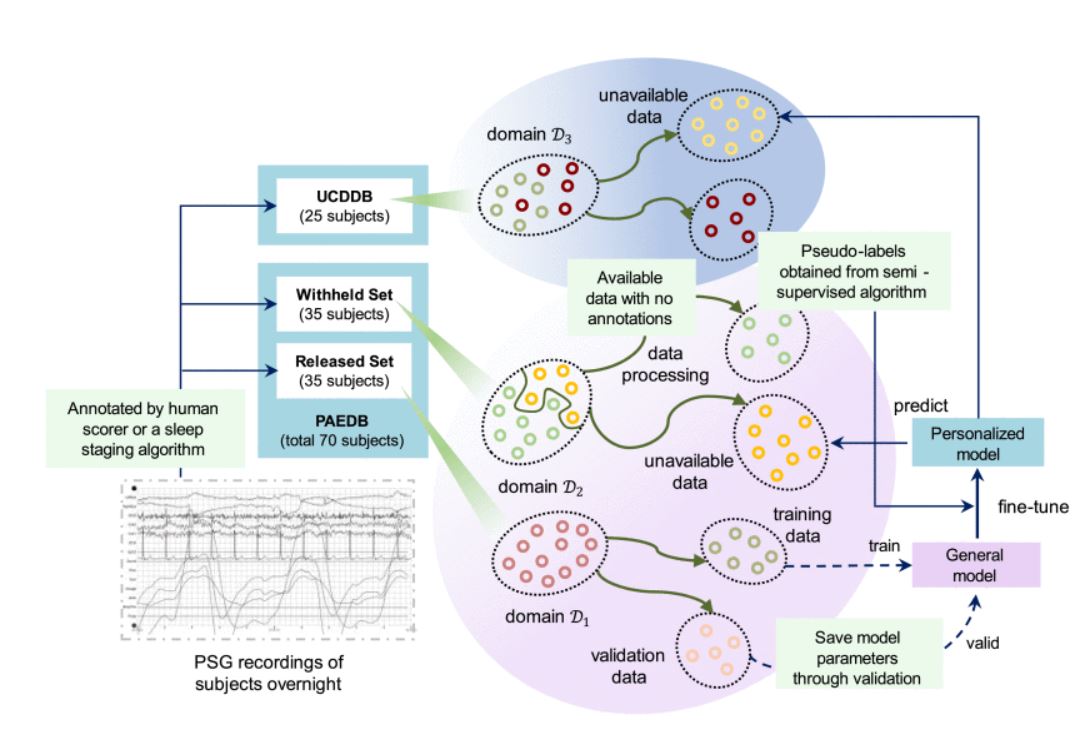
Recommended citation: Hu, Shuaicong, Liu Jian, Cuiwei Yang, Aiguo Wang, Kuanzheng Li, and Wenxin Liu. "Semi-supervised learning for low-cost personalized obstructive sleep apnea detection using unsupervised deep learning and single-lead electrocardiogram." IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics (2023).
Download Paper
[8] A multi-module algorithm for heartbeat classification based on unsupervised learning and adaptive feature transfer
Published in Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2024
This study proposes a multi-module heartbeat classification algorithm. Initially, unsupervised feature extractors are designed to extract rich features from unlabeled SD and TD data.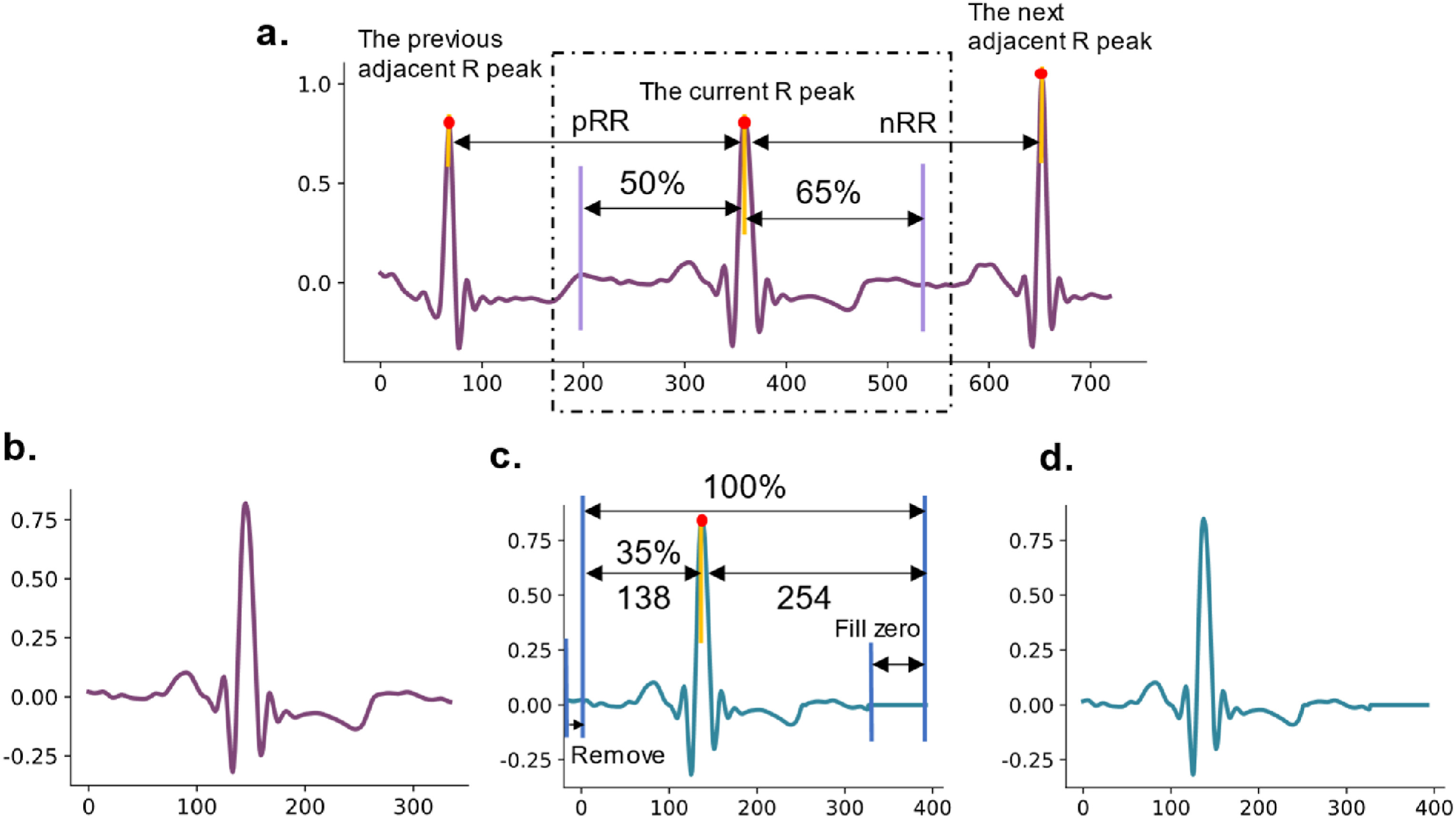
Recommended citation: Wang Yanan, Shuaicong Hu, Liu Jian, Gaoyan Zhong, and Cuiwei Yang. "A multi-module algorithm for heartbeat classification based on unsupervised learning and adaptive feature transfer." Computers in Biology and Medicine 170 (2024): 108072.
Download Paper
[9] Efficient Multi-View Fusion and Flexible Adaptation to View Missing in Cardiovascular System Signals
Published in Neural Networks, 2024
In this paper, the View-Centric Transformer (VCT) and Multitask Masked Autoencoder (M2AE) are specifically designed to emphasize the centrality of each view and harness unlabeled data to achieve superior fused representations.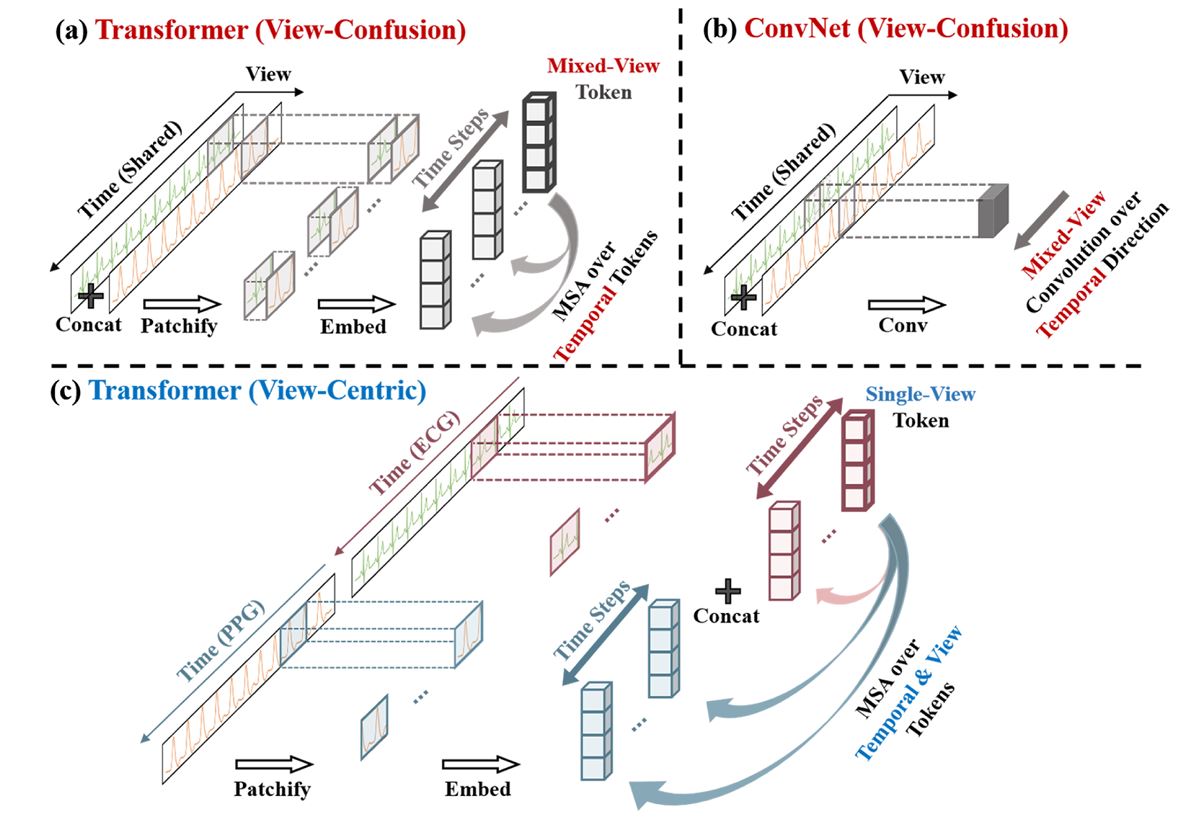
Recommended citation: Hu Qihan, Daomiao Wang, Hong Wu, Liu Jian, and Cuiwei Yang. "Efficient multi-view fusion and flexible adaptation to view missing in cardiovascular system signals." Neural Networks 181 (2025): 106760.
Download Paper
[10] IPCT-Net: Parallel information bottleneck modality fusion network for obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis
Published in Neural Networks, 2024
This paper develops a modality fusion representation enhancement (MFRE) framework adaptable to flexible modality fusion types with the objective of improving OSA diagnostic performance, and providing quantitative evidence for clinical diagnostic modality selection.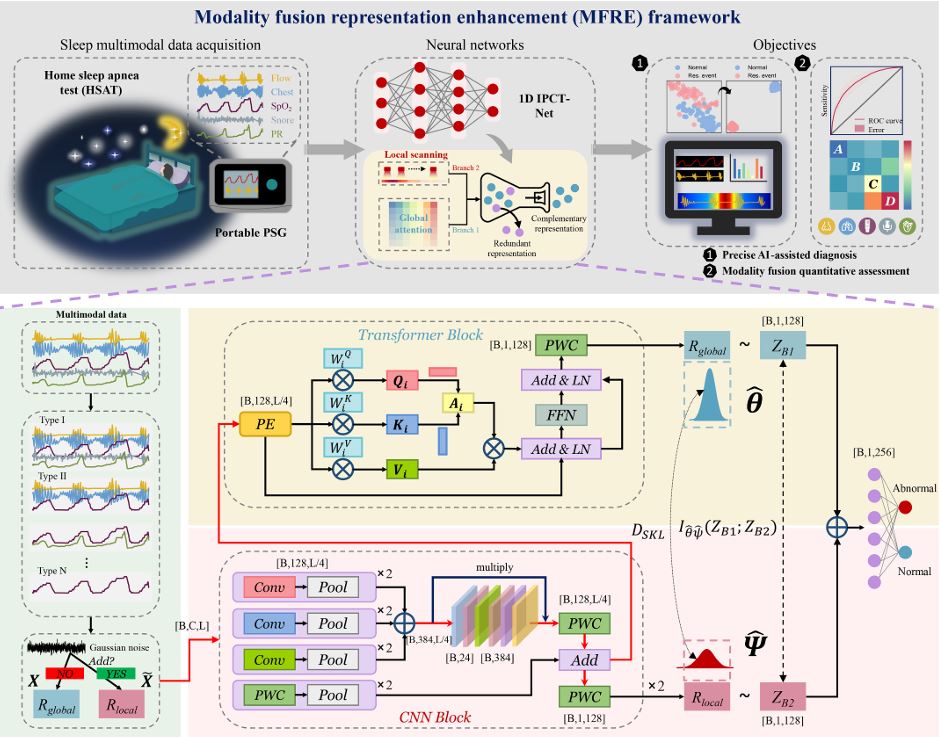
Recommended citation: Hu Shuaicong, Yanan Wang, Liu Jian, Zhaoqiang Cui, Cuiwei Yang, Zhifeng Yao, and Junbo Ge. "IPCT-Net: Parallel information bottleneck modality fusion network for obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis." Neural Networks (2024): 106836.
Download Paper
[11] An IoMT-Driven Framework for Precision Cardiovascular Assessment Incorporating Multiscale Perspectives and Microfiber Bragg Grating
Published in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024
Herein, we introduce an innovative Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) framework for personalized hemodynamic assessment, driven by advanced flexible sensing technologies and multi-scale modeling.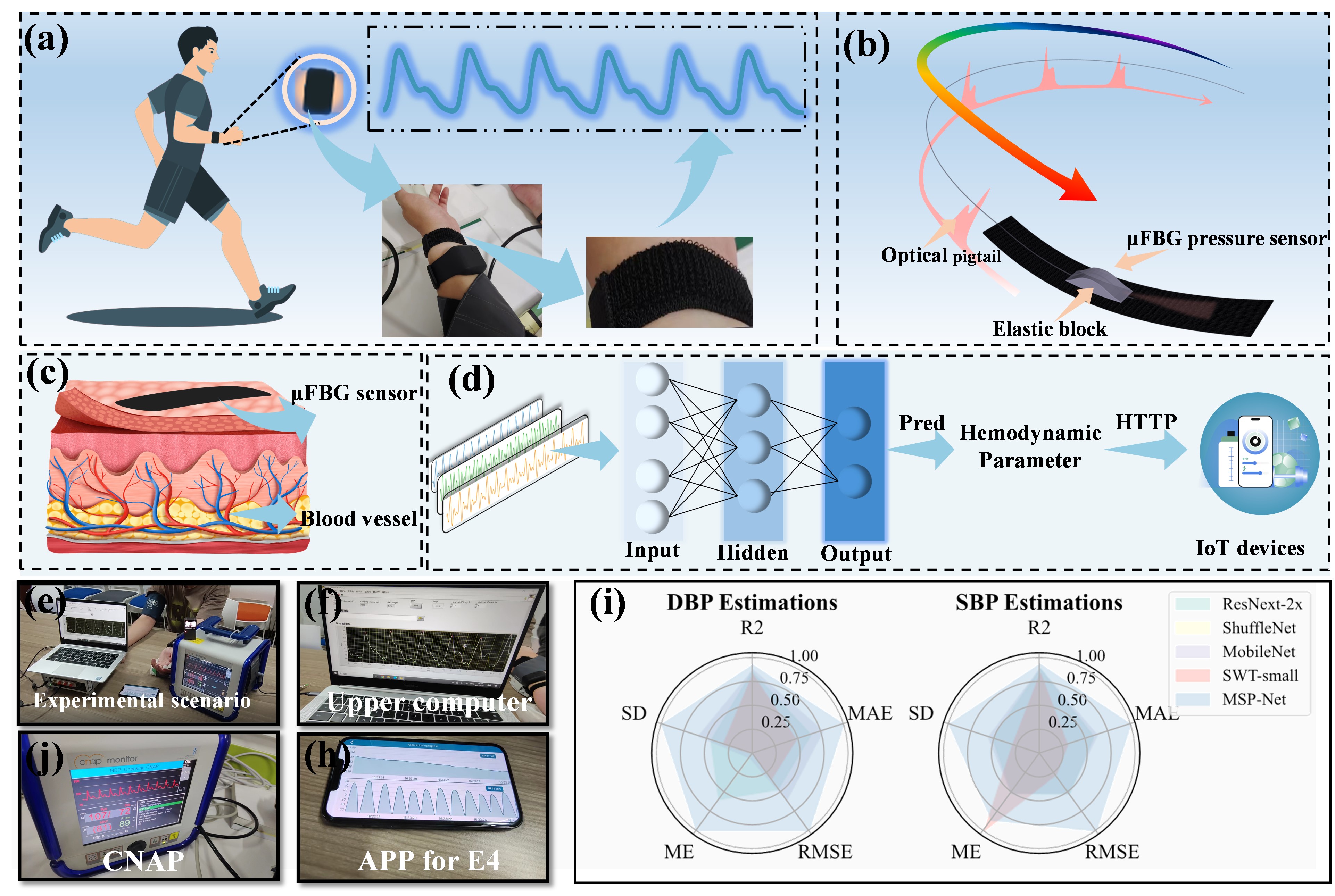
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, Hengtian Zhu, Wei Xiang, Shuaicong Hu, Qihan Hu, Daomiao Wang, Huan Yang, Zhengyi Mao, Fei Xu, and Cuiwei Yang. "An IoMT-Driven Framework for Precision Cardiovascular Assessment Incorporating Multiscale Perspectives and Microfiber Bragg Grating." IEEE Internet of Things Journal (2024).
Download Paper
[12] Personalized Blood Pressure Estimation using Multiview Fusion Information of Wearable Physiological Signals and Transfer Learning
Published in Applied Soft Computing, 2024
In this paper we propose a parallel cross-hybrid architecture that integrates a convolutional neural network backbone and a Mix-Transformer backbone. This model, grounded in multi-view physiological signals and personalized fine-tuning strategies, aims to estimate BP, facilitating the capture of physiological information across diverse receptive fields and enhancing network expressive capabilitie.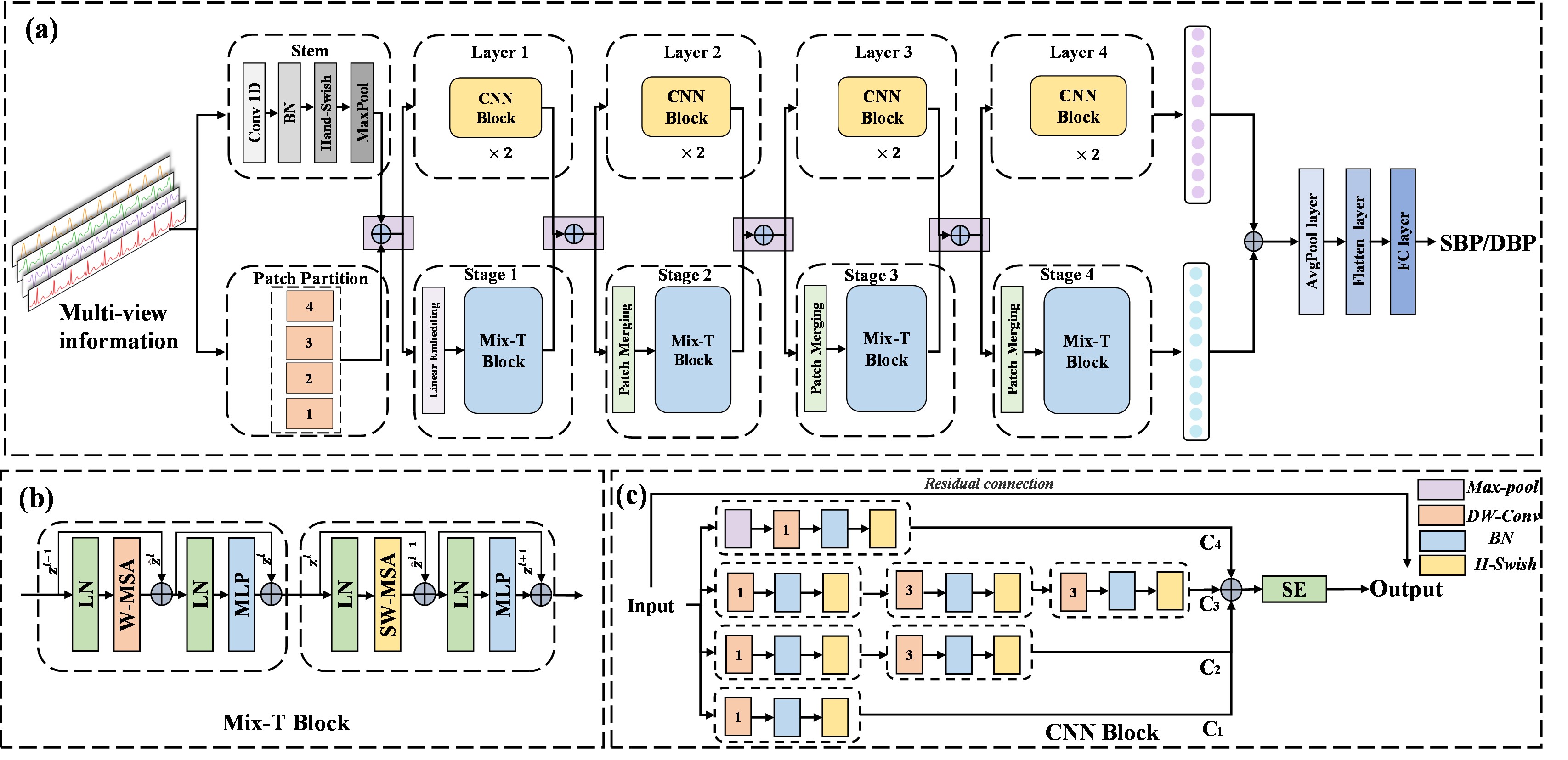
Recommended citation: Liu Jian, Shuaicong Hu, Yanan Wang, Wei Xiang, Qihan Hu, and Cuiwei Yang. "Personalized Blood Pressure Estimation using Multiview Fusion Information of Wearable Physiological Signals and Transfer Learning." Applied Soft Computing (2024): 112390.
Download Paper
[13] Preventing troublesome variability in clinical blood pressure measurement
Published in Journal of Human Hypertension, 2024
This study investigates the effect of six different measurement conditions (Quiet, Reading, Speaking, Deep Breathing, Moving, and Tapping) on BP readings in 30 healthy normotensive subjects. We hypothesize that non-standard conditions will result in significant deviations in BP measurements compared to the Quiet condition.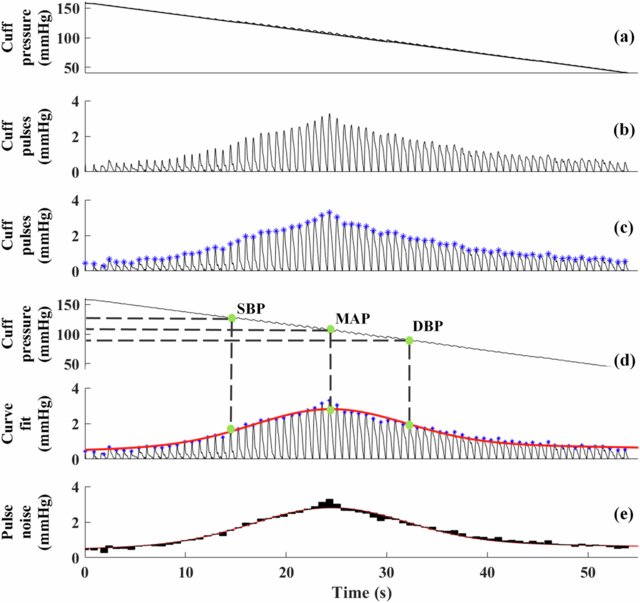
Recommended citation: Liu Chengyu, Liu Jian, Jianqing Li, and Alan Murray. "Preventing Troublesome Variability in Clinical Blood Pressure Measurement." Journal of Human Hypertension. (2024)
Download Paper
[14] LEAF-Net: A real-time fine-grained quality assessment system for physiological signals using lightweight evolutionary attention fusion
Published in Journal of Human Hypertension, 2025
We have devised an attention network capable of simulating localized to global dependency relationships. By training individually, a corresponding QA model is assigned to each pattern. Fine-grained labels for the signals are allocated through weakly supervised learning. The proposed lightweight model has undergone systematic deployment, accompanied by the development of an interactive interface.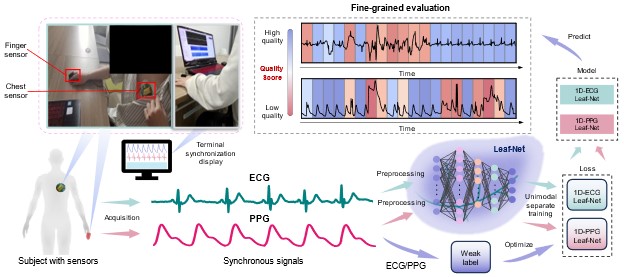
Recommended citation: Jian Liu, Shuaicong Hu, Yanan Wang, Qihan Hu, Daomiao Wang, Wei Xiang, Xujian Feng, and Cuiwei Yang. "LEAF-Net: A real-time fine-grained quality assessment system for physiological signals using lightweight evolutionary attention fusion" Expert Systems with Applications. (2025)
Download Paper
resource
LSMOE
🌟 Advanced Hemodynamic Parameter Estimation via the Lightweight Sparse Multi-Gate Mixture-of-Experts (LSMOE) Framework for Complex Multi-Task Scenarios 🌟
LEAF-Net
🌟 A novel lightweight attention network designed to address the challenge of high-resolution quality assessment (QA) in multimodal data 🌟
FACT-Net
A Two-Stage Fusion-CNN-Transformer Framework for ABP Signal Reconstruction in Cross-Platform Multi-Patient IoT Healthcare Systems
talks
2021 CINC ORAL
Published:
teaching
Medical Electronic Instruments
, Jiangwan Campus, Fudan University, Teaching Building A, 2023
Course Schedule and Key Points
📚 Overview
This course provides a comprehensive introduction to the characteristics, principles, and applications of medical instrumentation, with a focus on the measurement and processing of physiological signals such as bioelectric signals, neural activity, and cardiovascular metrics. The course combines foundational theories with practical applications and highlights advancements in both non-invasive and traditional measurement techniques.
🗓️ Schedule and Highlights
September 15
Chapter 1: Characteristics of Medical Instruments
Introduction to foundational concepts based on the textbook.September 22
Chapter 2: Measurement of Bioelectric Signals - Detection Part 1
Topics: Electrodes, Amplifiers, and Filtering Techniques.October 8
Assignment: Spectrum AnalysisOctober 13
Chapter 2: Measurement of Bioelectric Signals - Detection Part 2
Topics: Sensors and Practical Applications.October 20
Chapter 2: Measurement of Bioelectric Signals - Processing
Topics: Signal Processing Techniques, Noise Interference, and Suppression Methods.October 27
Chapter 2: Measurement of Bioelectric Signals - Electrocardiography (ECG)
Topics: Principles of ECG and ECG Machines.November 3
Chapter 3: Neural System Measurements - Part 1 (EEG)
Topics: Principles of Electroencephalography (EEG) (Lecture slides).November 10
Chapter 3: Neural System Measurements - Part 2 (EMG)
Topics: Principles of Electromyography (EMG) (Lecture slides).November 16
Special Topic 1: Advances in Continuous Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Measurement Technologies
Coverage of BCG, PPG, ICG, and related techniques.November 23
Assignment Submission: Spectrum AnalysisNovember 30
Special Topic 2: Comparative Analysis of Non-Contact vs. Traditional ECG Collection Methods
Discussion on Advantages and Limitations.
🎯 Key Learning Objectives
- Understand the basic characteristics and principles of medical instrumentation.
- Explore the detection and processing techniques for bioelectric signals, including electrodes, sensors, amplifiers, and noise suppression.
- Learn the principles and applications of neural measurement systems such as EEG and EMG.
- Gain insights into cutting-edge non-invasive measurement technologies, focusing on cardiovascular metrics like continuous blood pressure monitoring.
- Analyze the trade-offs between non-contact and traditional ECG techniques in clinical practice.
This course integrates theoretical knowledge with real-world applications, fostering a deeper understanding of modern medical instrumentation.
📍 Venue: Jiangwan Campus, Fudan University, Teaching Building A
📅 Course Dates: September 1, 2023 - January 15, 2024
📍 Location: Shanghai, CN
